Product Features

Highly stable temperature control
Standard control/heating and cooling control
Prevent overheating and overcooling in devices that require a high level of temperature stability, such as in an extrusion molding machine.
The following control methods can be selected according to the target device.
- Standard control (heating or cooling)
- Heating/cooling control (heating and cooling)
- Mix control (combination of standard control and heating-cooling control)
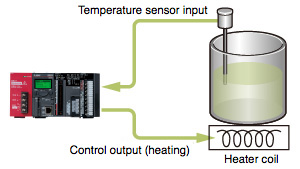
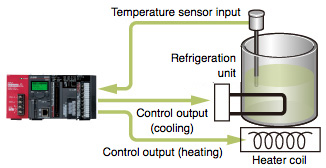
| ■ Example: Standard control (heating only) The temperature of the object is controlled by adjusting the heater output based on the PID calculations resulting from the temperature sensor input. | ■ Example: Heating-cooling control (heating and cooling elements controlled simultaneously) Heating is performed when the control object's temperature is lower than the target temperature, and cooling is performed when it is hotter or the humidity needs to be reduced. |
 |  |
Reduce running costs by taking advantage of the energy-saving effect
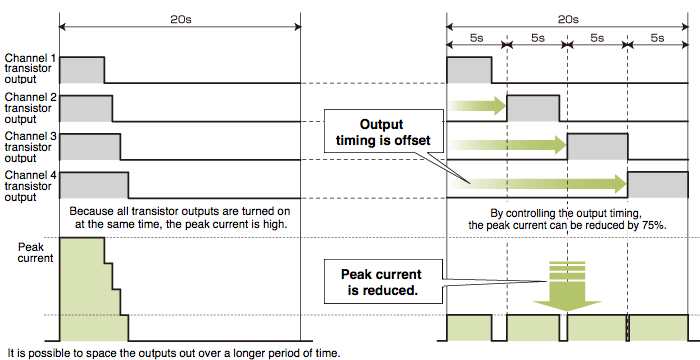
Peak current control function
The peak current control function reduces the peak current by automatically changing the upper-output limit value for each channel, while dividing the transistor output timing*1.
The energy conserved by reducing the peak current, such as a reduction in system power capacity and reduction in contracted power, can help to reduce running costs.
When two or more loads are being controlled, the peak current can be minimized by spreading the total load out over time.
| ■ Without peak current control function | ■ With peak current control function |
 | |
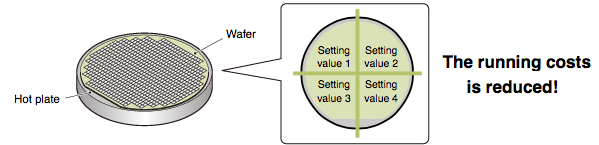
Ensures uniform temperature control
Simultaneous temperature rise function
Ensures uniform temperature control by synchronizing the temperature arrival times from multiple loops.
Perform a uniform temperature rise using two or more control loops without going over temperature or resulting in unexpected thermal expansion.
A "no idling" format increases energy efficiency and reduces running costs.
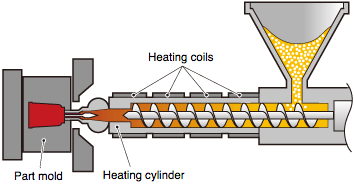
■ Example: Temperature control of injection molding machine
| ■ Without the simultaneous temperature rise function | ■ With the simultaneous temperature rise function |
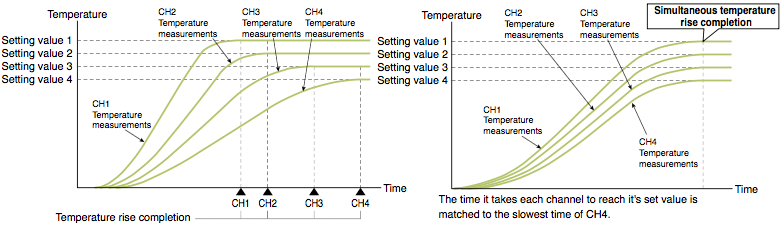 | |
Using this function, it is possible to coordinate the control of two or more loops to reach their target values (SV) at the same time. Control the simultaneous rise in temperature of separate loops by setting a channel group (Max. 2 groups).
This is an effective way to control applications where differing target temperature arrival times can result in undesirable temperature differentials.